The Road to Excellence: Seven Steps to Elevate Care Quality
7 Step Blueprint for Improving Care Quality
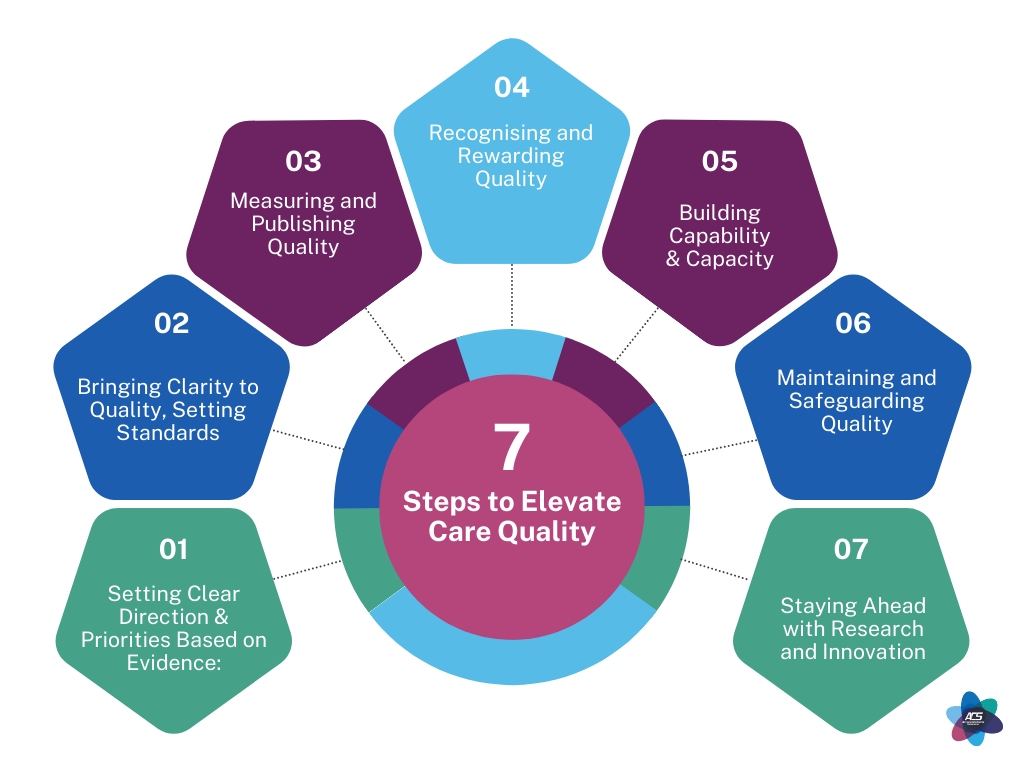
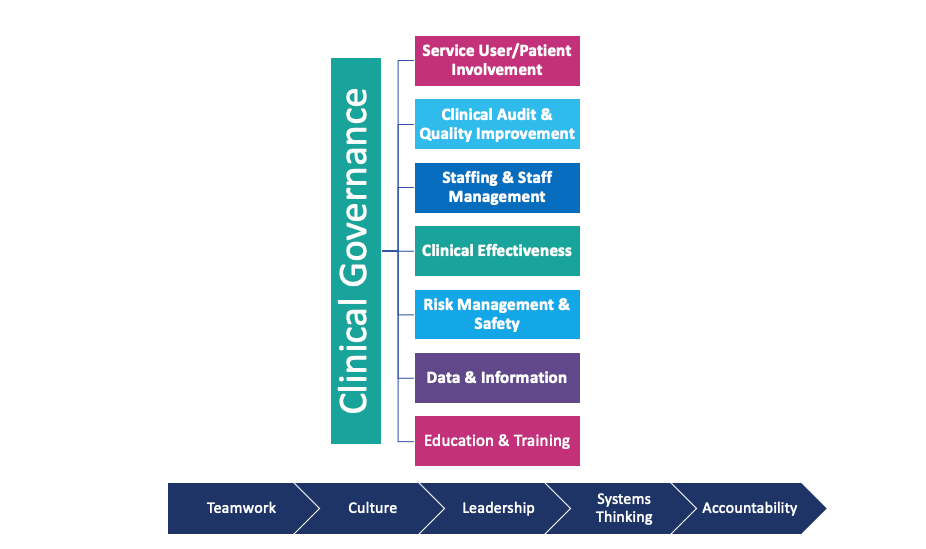
Quality care is the cornerstone of a robust healthcare system. The journey towards excellence is continuous, with each step building upon the last. The Health Foundation's adaptation of a Healthcare Quality Framework presents a seven-step path to not only maintain but elevate the quality of care. These steps provide a blueprint for healthcare professionals, organisations, and stakeholders to work collectively towards a shared goal, closing the care and quality gap. This blog post delves into these seven pivotal steps that can set a new standard for healthcare quality.
1.Setting Clear Direction and Priorities Based on Evidence:
To effectively implement quality improvement in healthcare, it's essential to set a clear direction and establish priorities based on evidence. Here's an expanded version of your statement to elaborate on these key points:
Establishing a Clear Direction:
- Initiating quality improvement in healthcare requires a well-defined direction. This involves understanding the current state of healthcare services and identifying areas that need improvement.
- Healthcare providers should conduct a thorough analysis of their services, considering factors such as patient outcomes, processes, efficiency, and staff performance.
- Setting a clear direction involves engaging with stakeholders, including patients, healthcare professionals, and partners, to gather insights and perspectives.
Prioritising Based on Evidence:
- Once the areas needing improvement are identified, priorities should be set based on robust evidence. This evidence can come from various sources, including clinical studies, patient feedback, and healthcare analytics.
- Prioritising based on evidence ensures that the focus is on areas that will have the most significant impact on patient care. This approach helps in allocating resources effectively and making informed decisions.
- The use of data analytics and evidence-based practices allows healthcare providers to track progress and adapt their strategies as needed.
Impact on Patient Care:
- The ultimate goal of setting clear direction and priorities in healthcare quality improvement is to enhance patient care. This includes improving patient safety, treatment outcomes, and overall patient experience.
- By focusing on evidence-based improvements, healthcare providers can ensure that changes made are meaningful and lead to better health outcomes.
- Continuous monitoring and evaluation of the impact of these improvements on patient care are crucial for sustaining progress and making necessary adjustments.
2.Bringing Clarity to Quality, Setting Standards
Bringing clarity to quality in healthcare and setting standards involves defining what high-quality care means, establishing clear and measurable benchmarks and metrics, ensuring consistency in care delivery across various settings, and accountability. This systematic approach not only fosters a culture of continuous improvement but also assures patients of receiving care that meets the highest possible standards.Expanding on the importance of setting standards for quality in healthcare involves several critical steps:
Defining Quality in Healthcare:
- The first step in bringing clarity to quality in healthcare is to define what high-quality care looks like. This involves considering various dimensions of quality, including patient safety, effectiveness, timeliness, efficiency, and equity.
- Quality in healthcare is multifaceted and should encompass the clinical and regulatory aspects of care, and the experiential aspects, such as patient satisfaction and engagement.
Establishing Clear Standards:
- Once quality is defined, the next step is to establish clear, measurable standards. These standards should be based on the latest clinical guidelines, best practices, and evidence-based procedures.
- Standards should be comprehensive, covering all aspects of healthcare delivery, from clinical care to administrative processes and patient experience.
- The establishment of standards must involve a wide range of stakeholders, including healthcare providers, patients, policy makers, and accreditation bodies.
Ensuring Consistency Across Settings:
- Quality standards should be consistent across all health and care settings, whether in hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities, or community-based services. This ensures that patients receive the same level of care regardless of where they are treated.
- Implementing uniform standards helps in creating a benchmark for all providers to strive towards. It also aids in minimising disparities in care delivery and outcomes.
Accountability and Improvement:
- With clear standards in place, healthcare providers can be held accountable for the quality of care they deliver. This accountability is crucial for driving improvements and ensuring compliance with the established benchmarks.
- Regular monitoring and assessment of compliance with these standards are essential. This could involve internal audits, patient feedback systems, and external accreditation processes.
- Standards should not be static; they need to be regularly reviewed and updated in light of new evidence, technological advancements, and changing patient needs.
3.Measuring and Publishing Quality
You cannot improve what you do not measure. Measuring and publishing quality outcomes in healthcare is essential for ensuring transparency, fostering accountability, and driving continuous improvement. By regularly assessing performance against a set of well-defined metrics, providers can identify both their strengths and areas for improvement, leading to strategic initiatives that enhance overall care quality.Expanding on the concept of measuring and publishing quality in healthcare involves several critical components:
The Importance of Measurement in Quality Improvement:
- Measurement is a cornerstone of quality improvement in healthcare. It is based on the principle that effective management of quality requires accurate, reliable data on performance.
- Regularly measuring key indicators of quality, such as patient outcomes, safety incidents, and service efficiency, provides a factual basis for assessing the current state of healthcare services.
- Without measurement, it is challenging to determine whether changes are leading to real improvements or to identify areas that require more attention.
Developing Effective Measurement Systems:
- To measure quality effectively, healthcare organizations need robust systems that can collect, analyze, and report data. These systems should encompass a wide range of metrics to provide a comprehensive view of performance.
- Choosing the right metrics is crucial. They should be relevant, measurable, and aligned with the organization's goals for quality improvement.
- The use of digital health technologies, such as electronic health records and data analytics tools, can greatly enhance the ability to track and analyze quality metrics.
Transparency through Publishing Quality Outcomes:
- Publishing quality outcomes serves several important purposes. Firstly, it promotes transparency, allowing patients and the public to see how well healthcare providers are performing.
- This transparency also fosters trust and accountability. Patients are more likely to trust healthcare providers who are open about their performance.
- Moreover, publishing outcomes can stimulate competition among healthcare providers, motivating them to improve their services to match or exceed industry benchmarks.
Driving Continuous Improvement:
- Regularly measuring and reporting on quality outcomes is not just about accountability; it's also a powerful tool for continuous improvement.
- By identifying areas where performance is lagging, healthcare providers can target their efforts to make meaningful improvements.
- Performance and quality reporting systems can highlight successes, which can be used as models for best practices, and areas needing improvement, guiding strategic initiatives to enhance the quality of care.
4.Recognising and Rewarding Quality
Recognising and rewarding quality plays a crucial role in motivating continuous improvement and setting high standards for care delivery. Through acknowledgment and incentives, providers are encouraged to strive for excellence, creating a benchmark for others and ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and a stronger culture of quality within healthcare organisations.Recognising and rewarding quality in healthcare involves several key aspects:
The Role of Recognition in Quality Improvement:
- Recognising high-quality care is a powerful motivator for healthcare providers. It validates their efforts and dedication to delivering superior care.
- Recognition can come in various forms, including formal awards, public acknowledgment, and positive feedback from patients and peers.
- This acknowledgment not only boosts morale but also encourages providers to maintain high standards and strive for excellence in patient care.
Incentivising Quality through Rewards:
- Beyond recognition, offering tangible rewards for high-quality care can further drive improvement efforts. These rewards could be financial, such as increased funding, or non-financial, like opportunities for professional development or additional resources.
- Incentives should be aligned with key quality metrics and designed to encourage behaviors and practices that directly improve patient outcomes and care efficiency.
- Well-designed reward systems can create a culture where quality is valued and prioritized, influencing the overall standard of care in an organisation.
Setting Benchmarks for Quality:
- Recognising and rewarding high-quality care also sets benchmarks for others in the healthcare system. It provides clear examples of what excellent care looks like and establishes goals for others to aspire to.
- Benchmarking against recognised high performers can stimulate healthy competition among providers, driving improvements across the board.
- Sharing best practices from recognised providers can also facilitate learning and improvement across different parts of the healthcare system.
Impact on Patient Care and Organisational Culture:
- Recognition and rewards can significantly impact the quality of patient care. When providers are motivated to excel, patients benefit from more attentive, effective, and compassionate care.
- This approach also fosters a positive organisational culture. A culture that values and rewards quality attracts and retains high-calibre care professionals who are committed to excellence.
- An environment that regularly acknowledges achievements in quality care reinforces the importance of continuous improvement, making it a fundamental part of the organisational ethos.
5.Maintaining and Safeguarding Quality
The mission for quality is not a one-time achievement .Maintaining and safeguarding quality is an ongoing commitment that requires vigilance, regular audits, patient feedback, peer reviews, and a proactive approach to prevent backsliding. By continuously monitoring and enhancing care practices, organisations can ensure that the quality of care they provide remains at the highest possible.The concept of maintaining and safeguarding quality in healthcare involves several essential components:
Understanding Quality as an Ongoing Commitment:
- Quality in healthcare is not a static goal but a continuous journey. It requires an ongoing commitment to maintain and improve care standards.
- This approach acknowledges that healthcare environments are dynamic, and what constitutes quality care can evolve due to factors like technological advancements, changing patient needs, and new medical knowledge.
Vigilance in Safeguarding Quality Gains:
- Safeguarding the improvements made in care quality is as important as achieving them. It involves being vigilant to ensure that the standards of care do not deteriorate over time.
- This vigilance requires a proactive approach, where potential issues are identified and addressed before they can lead to a decline in care quality.
- Healthcare providers need to be aware of and prepared to respond to both internal changes (like staffing or policy modifications) and external factors (such as evolving best practices or regulatory requirements).
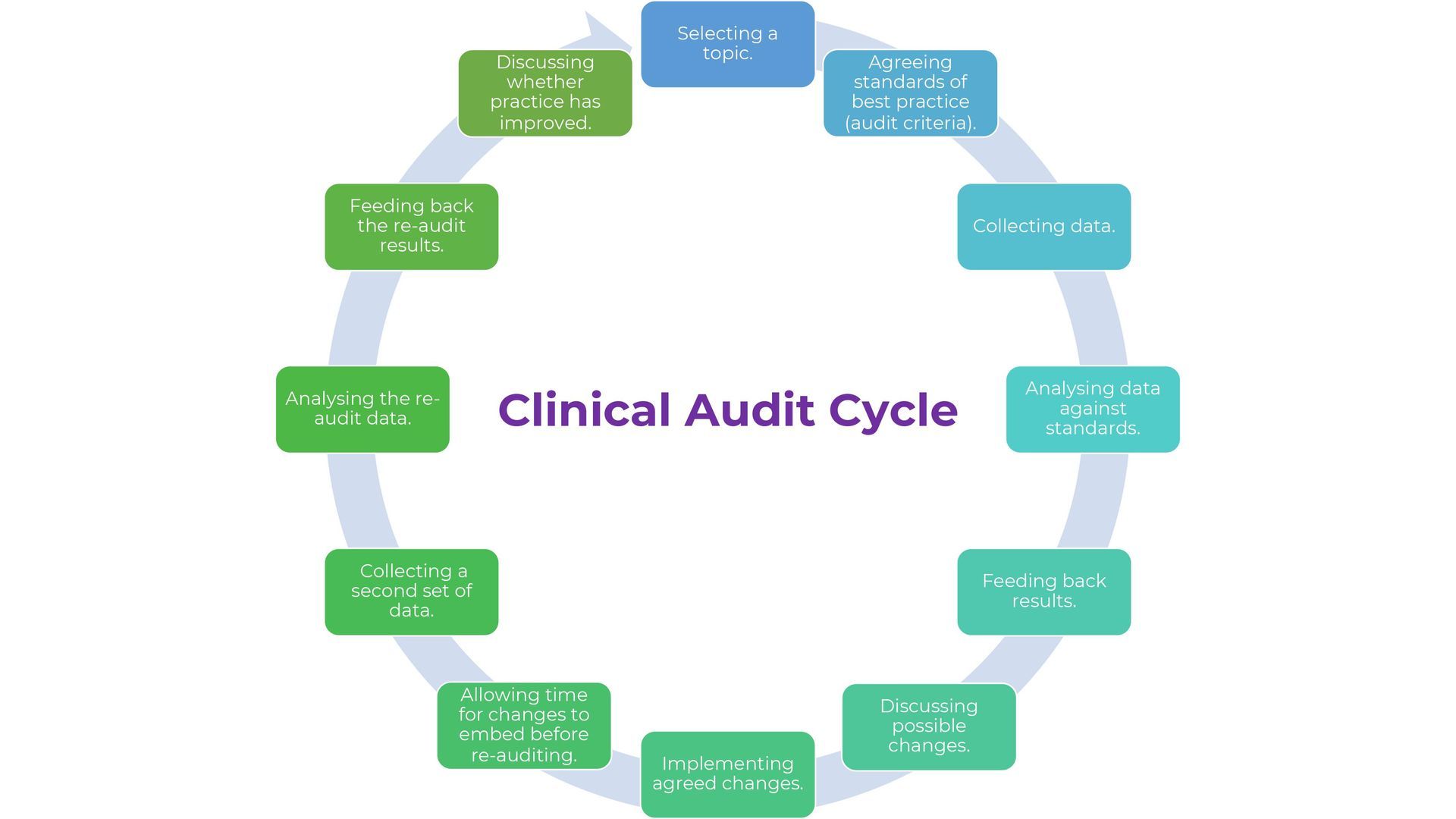
Regular Audits and Independent Assessments:
- Regular audits are crucial for maintaining quality in healthcare. These audits should assess various aspects of care delivery, including compliance with established clinical guidance, efficiency of care processes, and patient outcomes.
- Audits help in identifying areas where the standards may be slipping and provide opportunities for timely corrective actions.
- An independent assessment( such as those provided by ACS) is a great way to have an external , unbiased view of the quality of care provided .Sometimes the more complex the issues the more difficult it is to evaluate what is working, what isn’t and to find the reasons why. Healthcare involves many factors that lead to or prevent success. Those who self-evaluate will know many of these factors as they deal with them every day, but they may also lack the perspective to see larger patterns and interrelated issues , or even see organisational 'blind spots'
Incorporating Patient Feedback:
- Patient feedback is an invaluable tool for maintaining quality. Patients provide unique insights into their care experience, highlighting areas where improvements are needed.
- Regularly soliciting and acting upon patient feedback demonstrates a commitment to patient-centered care and helps in making necessary adjustments to enhance the quality of service.
Peer Reviews and Professional Development:
- Peer reviews are an effective way to ensure that healthcare providers maintain high standards. These reviews allow for sharing of best practices and provide a platform for constructive feedback.
- Continuous professional development is also essential. Healthcare providers should be encouraged and supported to keep their skills and knowledge up-to-date, ensuring they can deliver the highest quality care.
Creating a Culture of Quality:
- To sustain high-quality care, it's important to foster a culture that values and prioritises quality. This involves leadership commitment, ongoing training, and recognition of efforts towards quality improvement.
- In a culture that values quality, everyone from frontline staff to management is engaged in the process of maintaining and improving care standards.
6. Building Capability & Capacity
Building capability and capacity in healthcare is a multifaceted process that involves enhancing workforce competence, investing in leadership, fostering a culture that prioritises quality, providing adequate resources and infrastructure, and embracing innovation. These efforts are crucial for assuring the sustainability of quality improvements in healthcare.Building capability and capacity in healthcare involves several key components:
Enhancing Workforce Competence and Capability:
- The foundation of quality care lies in the competence and capability of the healthcare workforce. This includes not only clinical skills but also the ability to adapt to changing environments, new technologies, and evolving patient needs.
- Continuous skill development and training are essential for maintaining high standards of care. This involves regular updates in knowledge, care techniques, and the use of new technologies.
Investing in Leadership and Management:
- Effective leadership and management are crucial for driving quality improvement initiatives. Leaders must be equipped to inspire, guide, and support their teams in achieving quality goals.
- Investing in leadership development programs can help nurture the necessary skills in current and emerging leaders, such as strategic planning, decision-making, and change management.
Professional Development and Education:
- Continuous professional development is key to building the capacity of healthcare workers. This includes not only formal education but also on-the-job training, workshops, seminars, and conferences.
- Education and training should be tailored to the needs of the workforce, addressing both general competencies and specialised skills for specific roles.
Fostering a Culture that Prioritises Quality:
- Building a culture that prioritises quality is essential for sustainable improvements. This culture should value patient-centered care, teamwork, transparency, and continuous learning.
- Encouraging open communication, feedback, and collaboration among healthcare professionals helps in fostering a positive work environment where quality is a shared goal.
Resource Allocation and Infrastructure Support:
- Adequate resources and infrastructure are necessary to support the capability and capacity of the workforce. This includes having the right tools, technology, and facilities to provide high-quality care.
- Allocating resources wisely ensures that staff have what they need to perform their roles effectively, reducing stress and burnout, which can negatively impact quality.
Monitoring and Evaluating Progress:
- To ensure that efforts in building capability and capacity are effective, it is important to monitor and evaluate progress. This involves setting clear benchmarks and using performance metrics to assess improvements.
- Feedback mechanisms should be in place to gather insights from the workforce on the effectiveness of development programs and resource allocation.
Embracing Innovation and Best Practices:
- Staying abreast of innovations and adopting best practices are important aspects of building capability and capacity. This means being open to new ideas and approaches that can enhance care delivery.
- Encouraging a culture of innovation where staff are motivated to seek out and implement best practices can significantly contribute to the sustainability of quality improvements.
7. Staying Ahead with Research and Innovation
The final step is staying ahead with research and innovation in healthcare. This is vital for preparing the healthcare system to provide high-quality care as new challenges and technologies emerge. This involves a strong emphasis on research, fostering a culture of innovation, anticipating future challenges, adopting new technologies, integrating innovation into care delivery, collaborating on research and innovation efforts, and evaluating the impact of these innovations.
Emphasising Research in Healthcare:
- Staying ahead in healthcare heavily relies on a strong foundation in research. This involves not only clinical research but also research in healthcare systems, patient outcomes, and public health.
- Investing in research initiatives allows healthcare providers to base their practices on the latest scientific evidence, ensuring the care they provide is both effective and up-to-date.
- Collaborations with academic institutions, research organisations, and industry partners can enhance the scope and impact of research.
Fostering a Culture of Innovation:
- Innovation in healthcare is not just about new technologies but also about new ways of thinking and delivering care. This requires a culture that encourages creative problem-solving and continuous improvement.
- Healthcare organisations should create an environment where staff are encouraged to experiment with new ideas and approaches, with a focus on improving patient care and outcomes.
- Recognising and supporting innovative ideas from all levels of the organization can lead to groundbreaking improvements in care delivery.
Anticipating Future Challenges:
- Proactive planning for future challenges is essential . This involves understanding emerging trends, such as demographic shifts, changes in disease patterns, and advancements in technology.
- By anticipating these changes, healthcare systems can adapt their strategies and resources accordingly, ensuring they remain prepared to meet the evolving needs of their patients.
Adopting New Technologies:
- Keeping pace with technological advancements is crucial in modern healthcare. This includes not only medical devices and treatments but also information technology and data analytics tools.
- The adoption of new technologies can improve diagnostic accuracy, treatment effectiveness, and overall operational efficiency, leading to better patient care.
Integrating Innovation into Care Delivery:
- Innovation should be seamlessly integrated into everyday care delivery. This involves training staff on new technologies and methods, updating protocols and guidelines, and continuously monitoring the impact of these innovations.
- It's important that innovations are patient-centered, enhancing the experience and outcomes for patients while also improving the workflow for healthcare providers.
Collaborative Efforts in Research and Innovation:
- Collaborative efforts, both within the healthcare sector and with external partners, can significantly enhance the scope and effectiveness of research and innovation.
- Partnerships with technology companies, research institutions, and other healthcare organisations can lead to shared knowledge and resources, fostering breakthroughs in care delivery.
Evaluating the Impact of Innovations:
- It's crucial to regularly evaluate the impact of new innovations on care delivery and patient outcomes. This helps in understanding the effectiveness of these changes and guiding further improvements.
- Continuous evaluation also ensures that innovations are providing value and are aligned with the overarching goals of quality care and patient satisfaction.
The seven-step framework offers a strategic approach to enhancing care quality. From setting evidence-based directions to fostering a culture of excellence and innovation, each step is a stride towards a future where high-quality care is the norm, not the exception. Implementing these steps can bridge the quality gap, ensuring that every individual receives the best care possible. It's a collaborative effort that requires commitment from all levels of the system, and the reward—healthier, happier people—are well worth the effort.
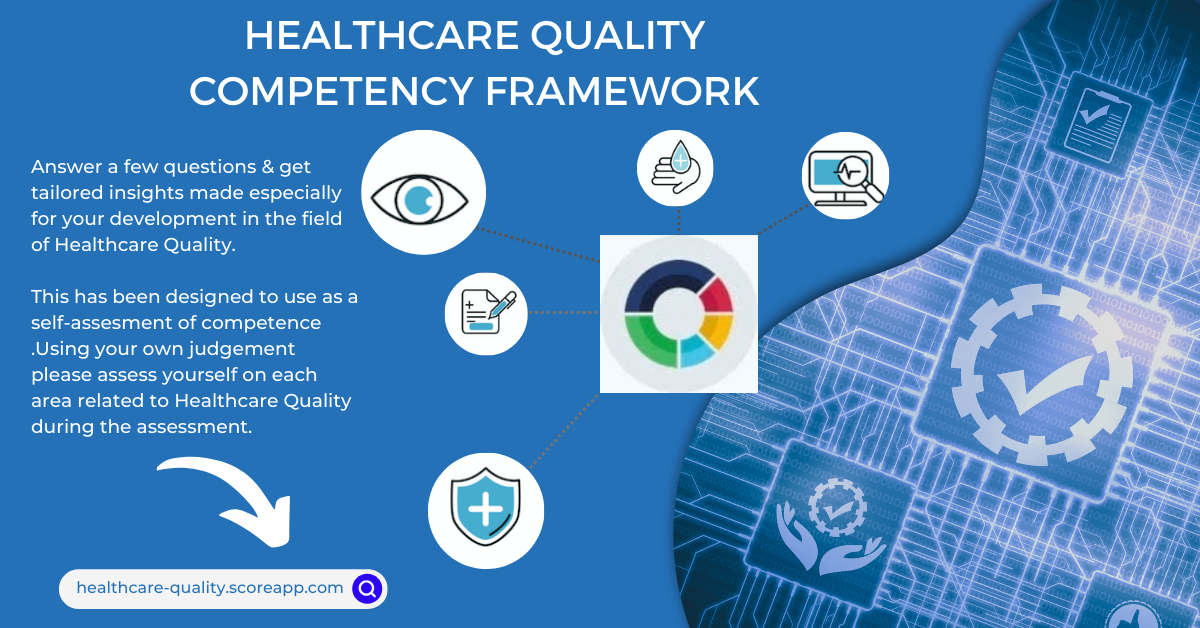
If you are looking to develop further in Healthcare Quality , why not tryout Healthcare Quality Self Assessment .Click on the image below to access , free of charge.
Email Us
For general enquiries & questions,
contact us via email
Book Free Consultation
Need some advice face to face? Book a free 30 minute MS Teams consultation
Share
CHECK OUT OUR OTHER BLOG POSTS
Knowledge Hub