5 Step Guide to Quality Evidence
Evaluating clinical evidence when time is of the essence
Evidence-based nursing is an approach to making quality decisions and providing nursing care based upon personal clinical expertise in combination with the most current, relevant research available on the topic. Clinical decisions should be based on:
Nursing and evidence-based decision making can also be limited by other factors such as ,financial and managerial constraints.However the barrier we hear about repeatedly is having time to access and evaluate clinical evidence. A nurse we spoke to recently had not had the time to evaluate a piece of clinical evidence since they had qualified nearly 9 years ago ! This has prompted us to create a really quick guide to picking out key information from a clinical paper. The best way to use this guide is to work through a clinical paper relevant to your field.It might also be an idea to have a highlighter handy to mark key points.
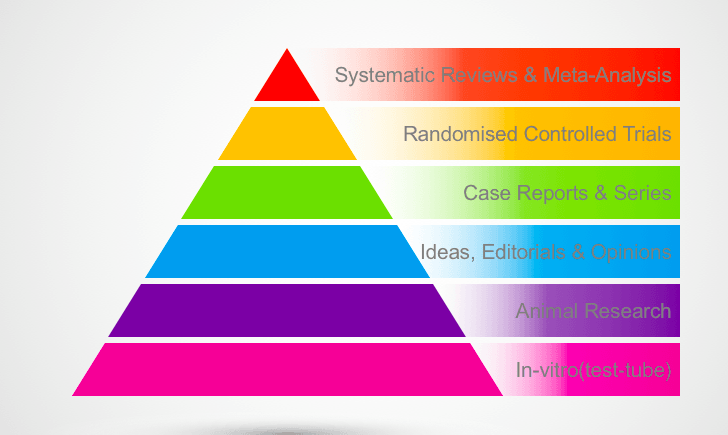
The Evidence Pyramid
Clinical literature reports a whole range of research, from in-vitro (test-tube lab studies not involving patients) right through to clinical trials involving hundreds of patients. This evidence can be divided up into different levels of quality, or importance when it comes to making a clinical decision. The evidence pyramid below is an indicator of the increasing quality of clinical evidence.The top 2 layers are the most clinically relevant i.e clinicians should put the most weight on this type of evidence or study result when deciding how to treat or manage a case.The bottom layers of evidence have the least clinical relevance.
There are a few basic types of clinical papers to consider
- Comparative Papers : Which compare with a placebo/traditional procedure or protocol
- Reviews:Which provide an overall conclusion based on previous research
- Cause and Effect: Looks at which factors significantly influence an outcome
- Surveys/questionnaires: Which are a compilation of results and conclusions from collected data
Other bits of information to look out for , which are not always obvious are a secondary positive outcome or a positive single observation
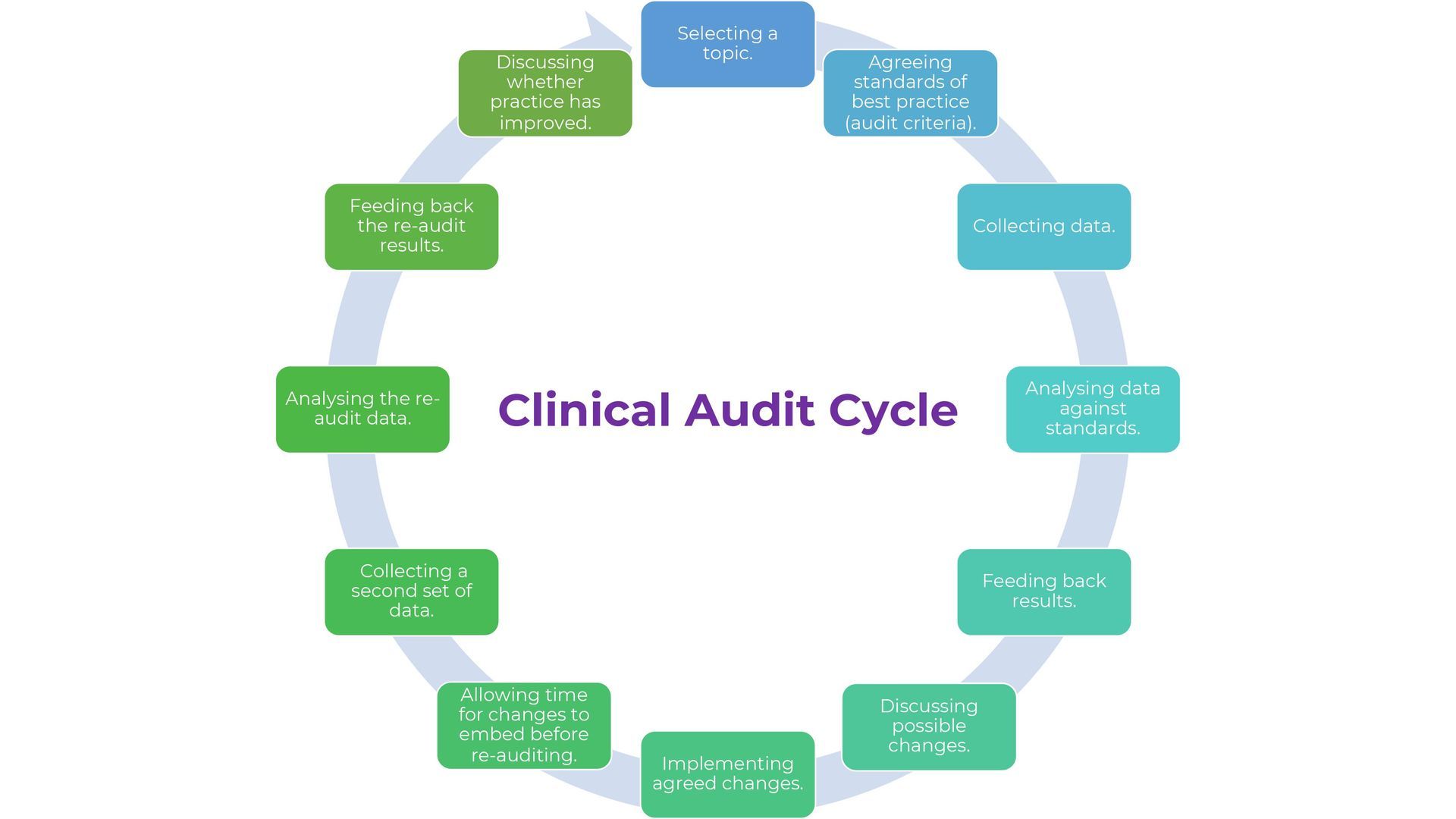
STEP-BY STEP GUIDE
READ IN THIS ORDER : It will take a short amount of time and help you glean the most relevant information from the evidence.
STEP 1: TITLE & ABSTRACT :Note the methodology, sample size, significant results and conclusion of the author(s)
STEP 2 : INTRODUCTION : Note the subject area being studied, purpose and what is being investigated, advantages of this study and finally check previous literature that’s referenced
STEP 3: CONCLUSION : This usually explains what the clinical significance of the results are.
STEP 5: DISCUSSION: How has the evidence moved knowledge on. It can explain any differences or similarities with previous study results .This section is where any drawbacks are discussed. It can also explain any new understanding from these results and what studies should be done next.
What is this telling me ?
Now you have read and highlighted the key points its now time to consider if the information being presented is any good .
Evidence Pyramid: TOP 3
- Systematic reviews -Comprehensive survey of highest levels of evidence in literature ,evidence is identified, appraised and summarised by a specific method
- Meta-analysis- Survey of similar studies , the results from studies are combined and analysed as if from 1 study.
- RCT (double-blinded) Patients are randomised to the treatment and control groups , the clinicians and patients are blinded to the treatment.
Sample Size & Statistical Significance
Sample Size = The bigger the better, P Value the smaller the better In other words:If p ≤ 0.05 Then p ≤ 5%(0.05 x 100 = 5%) meaning there is a less than 5% chance the result was a random fluctuation.
Impact Scale
This is a measure of the relative importance of a journal within its field .It's calculated from the number of times articles from the journal are cited ,over a preceding set time period.
AUTHOR SCALE :
Very similar to the evidence pyramid there is definitely a noticeable scale for quality of authors too.Look at the example below ranging from 1-6 NICE is an extremely reputable source of clinical evidence.
- NICE Quality Standards Advisory Committee Member (QSACs)
- Society chairperson
- Professors
- Senior lecturers/consultants
- Junior clinicians/research students
- Industry employees
Date & Origin:
Recognise centres of excellence in your both locally and globally , Where possible try to use recent papers, ideally<5 years old.
This is just a really brief introduction to evaluating clinical evidence and another tool to help in evidence- based care. Advanced Clinical Solutions can offer a more in-depth Clinical Evidence Workshop at your location ' Contact Us' to find out more.
Josie Winter BSc MSc -Clinical Director : Advanced Clinical Solution Ltd
www.advancedclinicalsolution.co.uk
01633 415 427
Email Us
For general enquiries & questions,
contact us via email
Book Free Consultation
Need some advice face to face? Book a free 30 minute MS Teams consultation
Share
CHECK OUT OUR OTHER BLOG POSTS
Knowledge Hub